Menu
Hot-Topics
February 19, 2026 | SCOTUS Reaffirms Fourth Amendment Standard for Police Responding to Household Emergencies
Month: July 2020
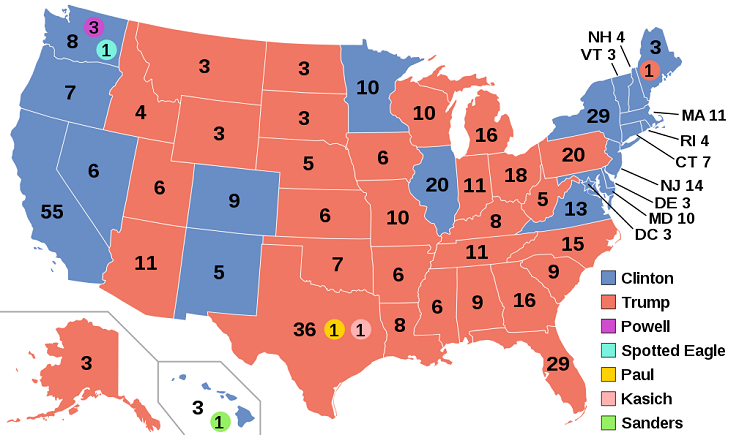
SCOTUS Unanimously Upholds Faithless Elector Laws
In Chiafalo v. Washington, 591 U. S. ____ (2020), the U.S. Supreme Court upheld state “faithless elector” laws. The justices unanimously ruled that states may enforce an elector’s pledge to support his party’s nominee—and the state voters�...

SCOTUS Issues Landmark Decision on President Trump’s Financial Records
In Trump v. Vance, 591 U. S. ____ (2020), the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that President Donald Trump is not immune to state subpoenas for his financial records. By a vote of 7-2, the Court held that Article II and the supremacy clause of the Constitut...

SCOTUS Rules Montana Funding Program Can’t Exclude Religious Schools
In Espinoza v. Montana Department of Revenue, 591 U. S. ____ (2020), a divided Supreme Court held that the application of the Montana Constitution’s “no-aid” provision to a state program providing tuition assistance to parents who send their c...

Divided Court Rules Trump Administration Can’t End DACA…For Now
In Department of Homeland Security v. Regents of the University of California, 591 U. S. ____ (2020), the U.S. Supreme Court held that the Department of Homeland Security’s decision to rescind the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) prog...
Previous Articles
SCOTUS Decision in Bowe v. United States Is First of the 2026 Term
by DONALD SCARINCI on February 5, 2026
In Bowe v. United States, 607 U.S. ___ (2026), the U.S. Supreme Court held that Title 28 U.S.C. § ...
SCOTUS Rules State Can’t Immunize Parties from Federal Civil Liability
by DONALD SCARINCI on January 29, 2026
In John Doe v. Dynamic Physical Therapy, LLC, 607 U.S. ____ (2025) the U.S. Supreme Court held that...
Supreme Court to Address Racial Discrimination in Jury Selection
by DONALD SCARINCI onWhile the U.S. Supreme Court has concluded oral arguments for the year, it continues to add cases t...
The Amendments
-
Amendment1
- Establishment ClauseFree Exercise Clause
- Freedom of Speech
- Freedoms of Press
- Freedom of Assembly, and Petitition
-
Amendment2
- The Right to Bear Arms
-
Amendment4
- Unreasonable Searches and Seizures
-
Amendment5
- Due Process
- Eminent Domain
- Rights of Criminal Defendants
Preamble to the Bill of Rights
Congress of the United States begun and held at the City of New-York, on Wednesday the fourth of March, one thousand seven hundred and eighty nine.
THE Conventions of a number of the States, having at the time of their adopting the Constitution, expressed a desire, in order to prevent misconstruction or abuse of its powers, that further declaratory and restrictive clauses should be added: And as extending the ground of public confidence in the Government, will best ensure the beneficent ends of its institution.
Awards





